
#Fibonacci sequence code python series
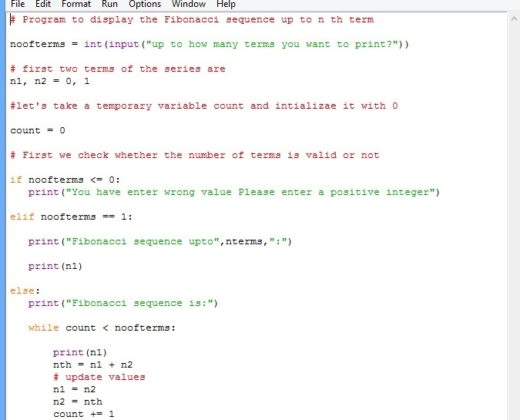
I believe this is the best (or nearly the best) solution: def fibo(n): The Fibonacci series is a sequence of numbers in which each is the sum of the two preceding ones, usually starting with 0 and 1. Better method of generating Fibonacci numbers The solution is to convert result of raw_input() into int like that: d = int(raw_input("How many numbers would you like to display"))Īnd everything will work unless you provide non-integer.īut there is better (shorter, more efficient, more encapsulated) method of generating Fibonacci numbers (see below). But range() expects expects integers, not strings, and Python does not convert it automatically (it leaves conversion to you). You assign string from the input into the d variable, and later you pass it to range(). The problem here is that here: d = raw_input("How many numbers would you like to display") Python Program to Print the Fibonacci sequence In this program.
#Fibonacci sequence code python how to
In the following section, you’ll see how to implement an algorithm to generate the Fibonacci sequence using iteration. # A sorter alternative for this three lines would be: Python Fibonacci Sequence: Iterative Approach1 Basic Javascript and Graphics: 26. 00:05 Now that you know the basics of how to generate the Fibonacci sequence, it’s time to go deeper and explore further the different ways to implement the underlying algorithm in Python. Print b # but I think several prints look better in this particular case.įor d in range(numbers - 2): # you already printed 2 numbers, now print 2 less Print a # you can write this as print "%i\n%i" % (a, b) # Note the number you enter should be > 2: you print 0,1 by default # In a robust program you should use try/except to catch wrong entries # as above as `range(int(numbers))` or in `int(raw_input())` # I personnally prefer this here, although you could put it

Numbers = raw_input("How many numbers would you like to display > ") In case that number is still smaller than c < n then we. In each iteration, it will calculate the next Fibonacci number c a+b and append it to the result. and we initialize it with: fibon (0,1,n, ). t2 is the second term in the list and n is the number of terms in the list. You simply have to use the following function: def fibon (a,b,n,result): c a+b result.append (c) if c < n: fibon (b,c,n,result) return result. Try this way for example: numbers = raw_input("How many numbers would you like to display")Įdit: I complete below the answer with additional code tuning (thanks to commenters): # one space will separate better visually question and entry in console I want to create a function that makes a so called super Fibonacci sequence which is a list of numbers, that from the third term onwards, every term is the sum of all the previous terms. It works but it is awful, unpythonic, whatever. One more thing: Do not use for d in range(d). The program is supposed to print 19, which is the fifth number of the Fibonacci sequence when using a litter size of 3. So convert d to an integer with: d = int(d)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
